Leukemia, commonly known as blood cancer, is a daunting diagnosis that disrupts the lives of patients and their families. This complex disease affects white blood cells, making it harder for the body to fight infections. Despite its challenges, advancements in medical science have brought hope to countless lives. In this blog, we’ll delve into leukemia’s types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options while addressing the all-important question—can leukemia be cured?
What is Leukemia?
Leukemia originates in the bone marrow, the body's blood cell production center. It results from mutations that lead to the excessive production of abnormal white blood cells. Unlike healthy cells, these abnormal cells fail to protect the body from infections and hinder the production of vital blood components like red blood cells and platelets.
This disruption manifests as symptoms such as fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and weight loss. Leukemia is broadly classified into acute (rapid progression) and chronic (slower progression) types, with further subtypes depending on the affected cells.
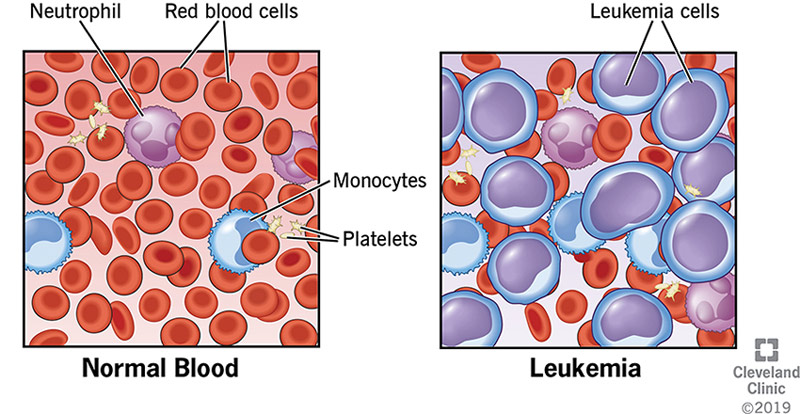 |
| Image Taken From Cleveland Clinic |
Types of Leukemia
Leukemia can be categorized into four primary types:
1. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
AML progresses quickly and affects myeloid cells, which produce red and white blood cells and platelets. Common symptoms include fatigue, bone pain, infections, and gum swelling.
2. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
CML progresses slower than AML and involves the overproduction of myeloid cells. Symptoms often include night sweats, abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss.
3. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL affects lymphoid cells responsible for immunity. It is more common in children but also occurs in adults. Symptoms include fever, frequent infections, and easy bruising.
4. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
CLL develops gradually and primarily affects older adults. Many patients remain symptom-free initially, but fatigue, swollen lymph nodes, and recurrent infections are common as the disease progresses.
What Causes Leukemia?
The exact causes of leukemia remain uncertain, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to its onset:
- Genetic Factors: Conditions like Down syndrome and genetic mutations in DNA repair mechanisms elevate the risk.
- Radiation Exposure: High radiation levels from nuclear accidents or repeated medical scans during childhood can increase vulnerability.
- Chemical Exposure: Prolonged contact with chemicals like benzene, often found in industrial products, can damage bone marrow.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of acute myeloid leukemia due to its harmful effect on blood cell DNA.
Symptoms of Leukemia
Leukemia symptoms vary by type but often overlap. Recognizing these signs early can make a significant difference:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections and fevers
- Unexplained weight loss
- Easy bruising or prolonged bleeding
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Bone pain or tenderness
Early detection is vital. If you or a loved one experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional without delay.
Is Leukemia Curable?
Leukemia’s curability depends on several factors, including its type, the patient’s age, overall health, and response to treatment. While not every case is curable, many patients achieve long-term remission. Below are the main treatment options:
1. Chemotherapy
A cornerstone of leukemia treatment, chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells. It’s administered in cycles, allowing the body to recover between sessions.
2. Targeted Therapy
This innovative treatment focuses on specific genetic mutations in cancer cells, offering fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
3. Stem Cell Transplantation
This procedure replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy donor cells, offering a potential cure, particularly for high-risk or relapsed leukemia.
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy enhances the immune system’s ability to fight cancer. CAR-T cell therapy is a notable example where modified T cells attack leukemia cells directly.
Why Early Detection Matters
Early diagnosis significantly improves treatment outcomes. Routine blood tests and monitoring symptoms can help catch the disease in its early stages, increasing the likelihood of successful treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Leukemia
Which type of leukemia has the highest cure rate?
Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) boasts cure rates exceeding 80% with early diagnosis and proper treatment.
Can leukemia return after treatment?
Yes, leukemia can relapse. Regular follow-ups and maintenance therapy can minimize this risk.
How important is diet during treatment?
While diet alone doesn’t cure leukemia, balanced nutrition aids recovery and helps manage treatment side effects.
Conclusion
Leukemia may be a challenging journey, but with advancements in medicine, many patients lead fulfilling lives post-treatment. Early detection, tailored therapies, and expert medical care are pivotal in managing this disease effectively.
And, Whether it’s understanding your symptoms or seeking advanced treatments, Arvachin Hospital is your trusted partner in health. Let’s fight leukemia together with compassion and care.



Comments
Post a Comment